Nota
Fare clic qui per scaricare il codice di esempio completo
Demo a torta2 #
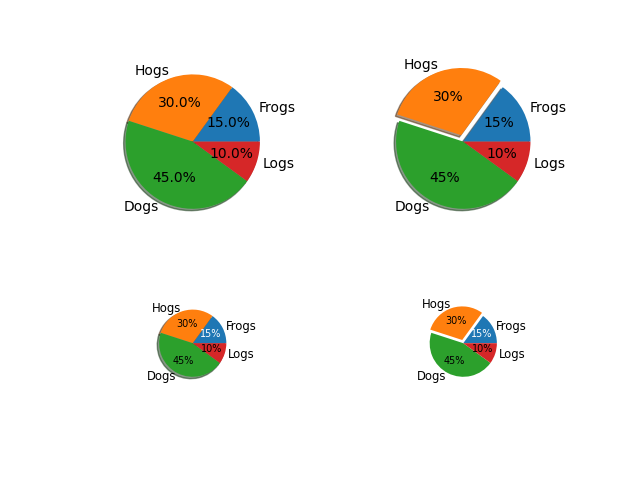
Crea un grafico a torta usando pie.
Questo esempio mostra alcune funzionalità del grafico a torta come etichette, dimensioni variabili, etichettatura automatica della percentuale, sfalsamento di una sezione e aggiunta di un'ombra.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Some data
labels = 'Frogs', 'Hogs', 'Dogs', 'Logs'
fracs = [15, 30, 45, 10]
# Make figure and axes
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2)
# A standard pie plot
axs[0, 0].pie(fracs, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True)
# Shift the second slice using explode
axs[0, 1].pie(fracs, labels=labels, autopct='%.0f%%', shadow=True,
explode=(0, 0.1, 0, 0))
# Adapt radius and text size for a smaller pie
patches, texts, autotexts = axs[1, 0].pie(fracs, labels=labels,
autopct='%.0f%%',
textprops={'size': 'smaller'},
shadow=True, radius=0.5)
# Make percent texts even smaller
plt.setp(autotexts, size='x-small')
autotexts[0].set_color('white')
# Use a smaller explode and turn of the shadow for better visibility
patches, texts, autotexts = axs[1, 1].pie(fracs, labels=labels,
autopct='%.0f%%',
textprops={'size': 'smaller'},
shadow=False, radius=0.5,
explode=(0, 0.05, 0, 0))
plt.setp(autotexts, size='x-small')
autotexts[0].set_color('white')
plt.show()
Riferimenti
L'uso delle seguenti funzioni, metodi, classi e moduli è mostrato in questo esempio: