Nota
Fare clic qui per scaricare il codice di esempio completo
Il formattatore di tick predefinito #
L'esempio mostra l'uso dell'impostazione predefinita ScalarFormattercon impostazioni diverse.
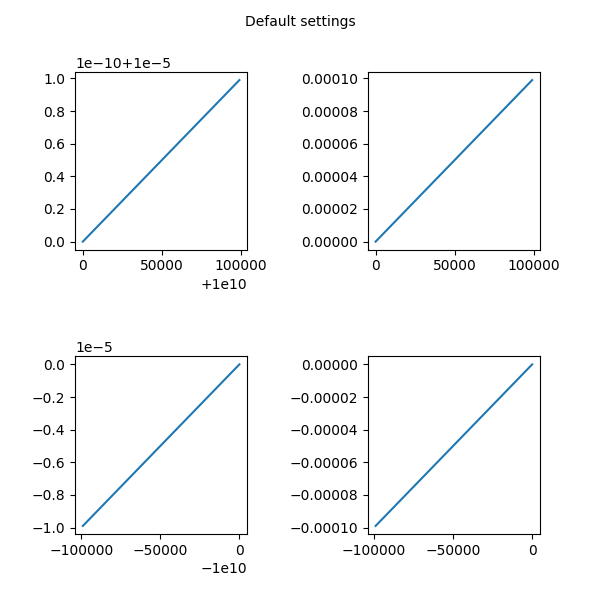
Esempio 1: Predefinito
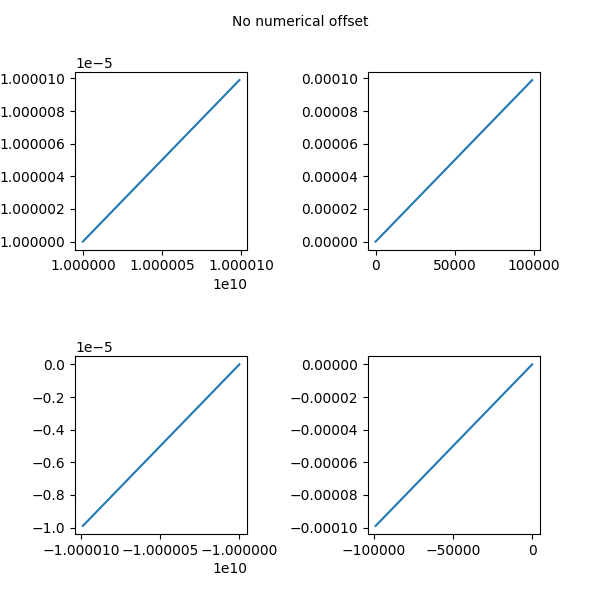
Esempio 2: senza offset numerico
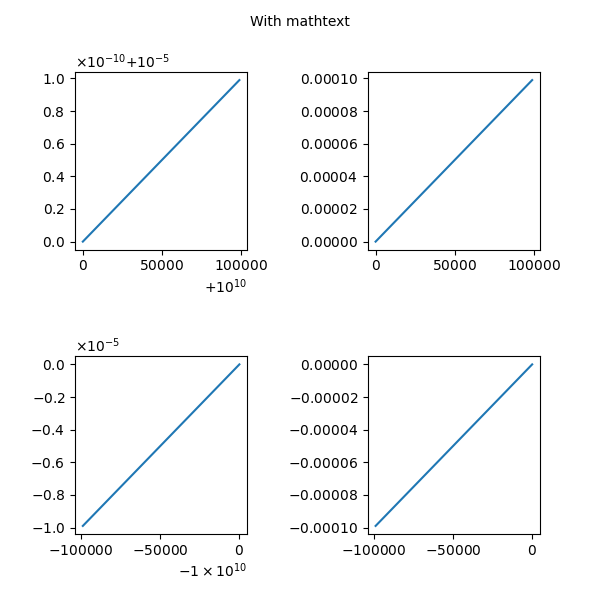
Esempio 3: Con Mathtext
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
Esempio 1
x = np.arange(0, 1, .01)
fig, [[ax1, ax2], [ax3, ax4]] = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(6, 6))
fig.text(0.5, 0.975, 'Default settings',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='top')
ax1.plot(x * 1e5 + 1e10, x * 1e-10 + 1e-5)
ax2.plot(x * 1e5, x * 1e-4)
ax3.plot(-x * 1e5 - 1e10, -x * 1e-5 - 1e-10)
ax4.plot(-x * 1e5, -x * 1e-4)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.7, hspace=0.6)
Esempio 2
x = np.arange(0, 1, .01)
fig, [[ax1, ax2], [ax3, ax4]] = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(6, 6))
fig.text(0.5, 0.975, 'No numerical offset',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='top')
ax1.plot(x * 1e5 + 1e10, x * 1e-10 + 1e-5)
ax1.ticklabel_format(useOffset=False)
ax2.plot(x * 1e5, x * 1e-4)
ax2.ticklabel_format(useOffset=False)
ax3.plot(-x * 1e5 - 1e10, -x * 1e-5 - 1e-10)
ax3.ticklabel_format(useOffset=False)
ax4.plot(-x * 1e5, -x * 1e-4)
ax4.ticklabel_format(useOffset=False)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.7, hspace=0.6)
Esempio 3
x = np.arange(0, 1, .01)
fig, [[ax1, ax2], [ax3, ax4]] = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(6, 6))
fig.text(0.5, 0.975, 'With mathtext',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='top')
ax1.plot(x * 1e5 + 1e10, x * 1e-10 + 1e-5)
ax1.ticklabel_format(useMathText=True)
ax2.plot(x * 1e5, x * 1e-4)
ax2.ticklabel_format(useMathText=True)
ax3.plot(-x * 1e5 - 1e10, -x * 1e-5 - 1e-10)
ax3.ticklabel_format(useMathText=True)
ax4.plot(-x * 1e5, -x * 1e-4)
ax4.ticklabel_format(useMathText=True)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.7, hspace=0.6)
plt.show()
Tempo di esecuzione totale dello script: (0 minuti 1,866 secondi)