Nota
Fare clic qui per scaricare il codice di esempio completo
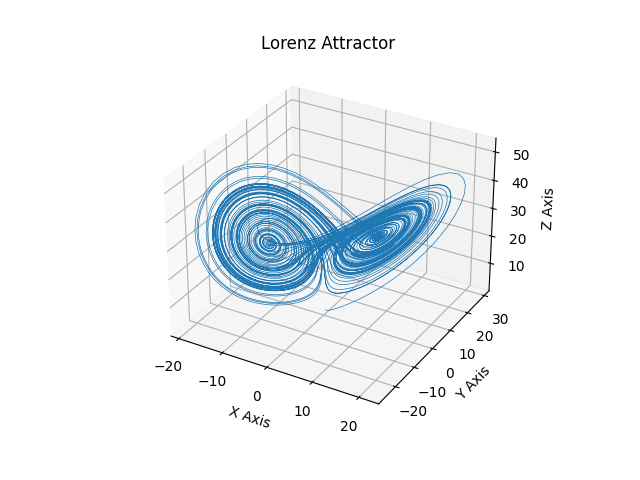
Lorenz Attrattore #
Questo è un esempio di tracciare il "Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow" di Edward Lorenz del 1963 in uno spazio tridimensionale usando mplot3d.
Nota
Poiché si tratta di una semplice ODE non lineare, sarebbe più semplice utilizzare il risolutore ODE di SciPy, ma questo approccio dipende solo da NumPy.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def lorenz(xyz, *, s=10, r=28, b=2.667):
"""
Parameters
----------
xyz : array-like, shape (3,)
Point of interest in three dimensional space.
s, r, b : float
Parameters defining the Lorenz attractor.
Returns
-------
xyz_dot : array, shape (3,)
Values of the Lorenz attractor's partial derivatives at *xyz*.
"""
x, y, z = xyz
x_dot = s*(y - x)
y_dot = r*x - y - x*z
z_dot = x*y - b*z
return np.array([x_dot, y_dot, z_dot])
dt = 0.01
num_steps = 10000
xyzs = np.empty((num_steps + 1, 3)) # Need one more for the initial values
xyzs[0] = (0., 1., 1.05) # Set initial values
# Step through "time", calculating the partial derivatives at the current point
# and using them to estimate the next point
for i in range(num_steps):
xyzs[i + 1] = xyzs[i] + lorenz(xyzs[i]) * dt
# Plot
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.plot(*xyzs.T, lw=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Axis")
ax.set_zlabel("Z Axis")
ax.set_title("Lorenz Attractor")
plt.show()